The financial world has undergone a transformative shift over the past few decades. The slow decline of fiat currency and the corresponding rise of cryptocurrencies have been notable markers of this change. This article explores the reasons behind the weakening hold of fiat money and the potential of cryptocurrencies to reshape the future of money.
1. Historical Trust in Fiat Currency
2. Why There Was Trust in Fiat?
3. Challenges Facing Fiat Currency
4. Cryptocurrency’s Edge Over Fiat
5. The Mass Adoption of Cryptocurrencies
6. Hurdles Cryptocurrencies Still Have to Face
7. Conclusion
Historical Trust in Fiat Currency
The financial landscape has always been in a state of flux, with numerous systems and methods being used to facilitate trade and maintain economic stability. Central to many of these systems, particularly in the modern era, has been fiat currency. But what is it about this form of money that has engendered trust for so long?
Understanding Fiat Currency
Before delving into the history, it’s essential to clarify what fiat money is. Unlike commodity money (like gold or silver coins), fiat currency has no intrinsic value. Instead, its worth is derived primarily from the trust and confidence of the people who use it. It is not backed by a physical commodity but rather by the government that issued it.
Historical Overview
Ancient Precursors: Ancient civilizations like China had early versions of fiat currency. Paper money in Yuan Dynasty China, for instance, was backed by the empire’s decree rather than tangible goods.
Gold Standard Era: Up until the 20th century, many global currencies were tied to the gold standard, meaning they could be exchanged for a specified amount of gold. However, the restrictions of this system made economic policy challenging, especially during recessions.
Bretton Woods & The Move Away from Gold: After World War II, the Bretton Woods Agreement was established, pegging various currencies to the US dollar, which was convertible to gold. This system lasted until 1971 when President Richard Nixon announced that the US would no longer exchange dollars for gold, ushering in the era of pure fiat money.
Why There Was Trust in Fiat?
Several factors have helped create trust in fiat currencies throughout history:
Government Backing: The foremost factor is the assurance that a nation’s government supports the currency. When a government is stable, its fiat currency usually enjoys more trust.
Legal Tender Laws: Many countries have laws mandating that their fiat currency must be accepted for all public and private debts.
Economic Systems: Central banks can influence a fiat currency’s value and purchasing power through monetary policy. Their actions, especially in stable economies, can foster trust in the currency.
Cultural Acceptance: Over time, as societies became accustomed to using government-backed notes and coins for transactions, the cultural trust in fiat currency grew.
Challenges and Critiques
Despite its historical prominence, fiat currency has faced challenges and criticisms. Because its value isn’t tied to a physical commodity, some argue it’s more susceptible to inflation, especially if a government prints money recklessly. Moreover, global economic crises, like those of 2008, have spurred debates about fiat money’s viability and the possibility of alternative financial systems.
Challenges Facing Fiat Currency
Fiat currency, which represents the money issued by a government that isn’t based on a physical commodity but rather the trust of its users, has been the dominant form of money for decades. While it offers flexibility and adaptability, especially in terms of monetary policy, the fiat system is not without its challenges.
Inflation and Hyperinflation
Inflation occurs when the general level of prices rises, leading to a decrease in purchasing power. This can be due to several factors, such as an increase in the money supply without a corresponding increase in goods and services.
Mild inflation is often seen as a sign of a healthy economy. However, excessive inflation or hyperinflation can devastate savings, disrupt economic planning, and lead to a loss of faith in the currency. Countries like Zimbabwe and Venezuela have experienced the debilitating effects of hyperinflation.
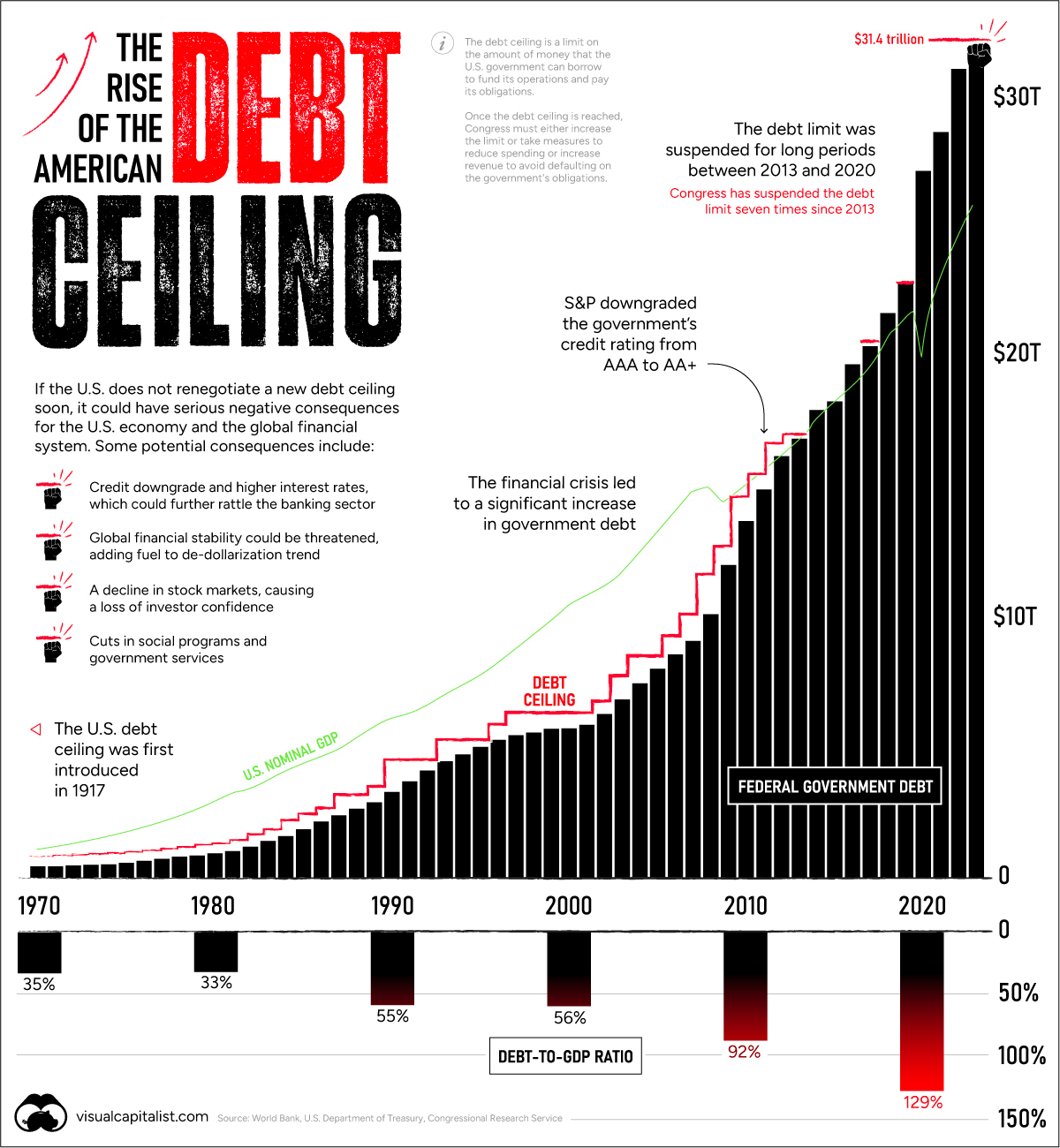
National Debt Levels
Many nations have taken on significant levels of debt, especially in response to economic recessions or to finance public projects.
While debt in itself isn’t necessarily problematic, concerns arise when countries accumulate unsustainable debt levels. This can lead to doubts about a nation’s ability to service its debt, which in turn can undermine confidence in its currency.
Dependency on Centralized Institutions
The fiat system heavily relies on centralized institutions like central banks. While these entities can stabilize an economy, they also hold significant power over monetary policy.
If these institutions make poor decisions or are perceived as being corrupt, it can diminish trust in the entire fiat system. The 2008 financial crisis, for example, led to widespread skepticism about centralized financial systems and institutions.
Political Instability and Geopolitical Tensions
Currency values can be influenced by political events and tensions, both within countries and on the international stage.
Political instability, be it due to elections, policy changes, or international conflicts, can create volatility in fiat currency values. Such instability can make trade and investment riskier and more unpredictable.
The Rise of Alternatives
Technological advancements and skepticism towards traditional financial systems have led to the rise of alternative forms of money, like cryptocurrencies.
As more people and institutions invest in and use cryptocurrencies, there’s potential for decreased reliance on and trust in fiat currencies. Moreover, technologies like blockchain offer transparency and decentralization, making them appealing to many.
The Problem of Trust
Fiat currencies fundamentally rely on trust. Without trust in the issuing government and its economic policies, the currency loses its value.
In times of crisis, if the public loses faith in the government’s ability to manage the economy, a rush to withdraw money or convert it to more stable currencies or assets can occur, leading to potential economic collapse.
Cryptocurrency’s Edge Over Fiat
In the vast and evolving realm of finance, the emergence of cryptocurrency has sparked a revolution. A stark contrast to traditional fiat currencies, digital or cryptocurrencies present a range of advantages that position them uniquely in the global monetary ecosystem. Here’s a closer look at the aspects where cryptocurrency seemingly has an edge over its more traditional counterpart.
Decentralization
Unlike fiat currencies that are issued and regulated by centralized governments and financial institutions, many cryptocurrencies operate on decentralized platforms.
This decentralization offers freedom from potential government interference, manipulation, or regulation. It also reduces the risk of mismanagement that can lead to financial crises.
Limited Supply
Most cryptocurrencies, like Bitcoin and Stohn Coin, have a predetermined supply, limiting the total number of coins that can ever be in circulation.
This scarcity contrasts with fiat money systems where central banks can print more money, leading to inflation. A capped supply can act as a hedge against the devaluation of money.
Cross-border Transactions
Cryptocurrencies can be sent and received anywhere in the world, and transactions can be completed faster than traditional banking systems or money transfer services.
This global reach and speed can revolutionize international business, reducing waiting times and transaction fees.
Inclusion and Accessibility
Cryptocurrencies offer financial inclusion in regions underserved by traditional banking systems. With just a smartphone and internet access, anyone can participate in the global economy.
Millions of unbanked individuals can now have access to financial services, fostering economic growth in previously marginalized communities.
Security and Transparency
Leveraging blockchain technology, cryptocurrencies offer a more secure transaction system than traditional banking. The decentralized and cryptographic nature of blockchains makes them immutable, ensuring that once data has been added, it cannot be changed without altering all subsequent blocks, which is nearly impossible.
This robust security feature minimizes fraud and unauthorized activities, and the transparency of the blockchain can build trust among its users.
Potential for Innovation
The cryptocurrency ecosystem is not just about digital money. It’s a breeding ground for innovative financial products and services, especially within the realm of Decentralized Finance (DeFi).
From decentralized lending platforms to yield farming, the crypto space is at the forefront of financial innovation, offering users more control over their assets and financial decisions.
Sovereignty over Personal Finances
Cryptocurrencies offer individuals sovereignty over their funds, allowing them to control and manage their wealth without intermediaries.
This direct control can lead to more responsible and aware financial behavior, as individuals recognize the full responsibility of managing their assets.
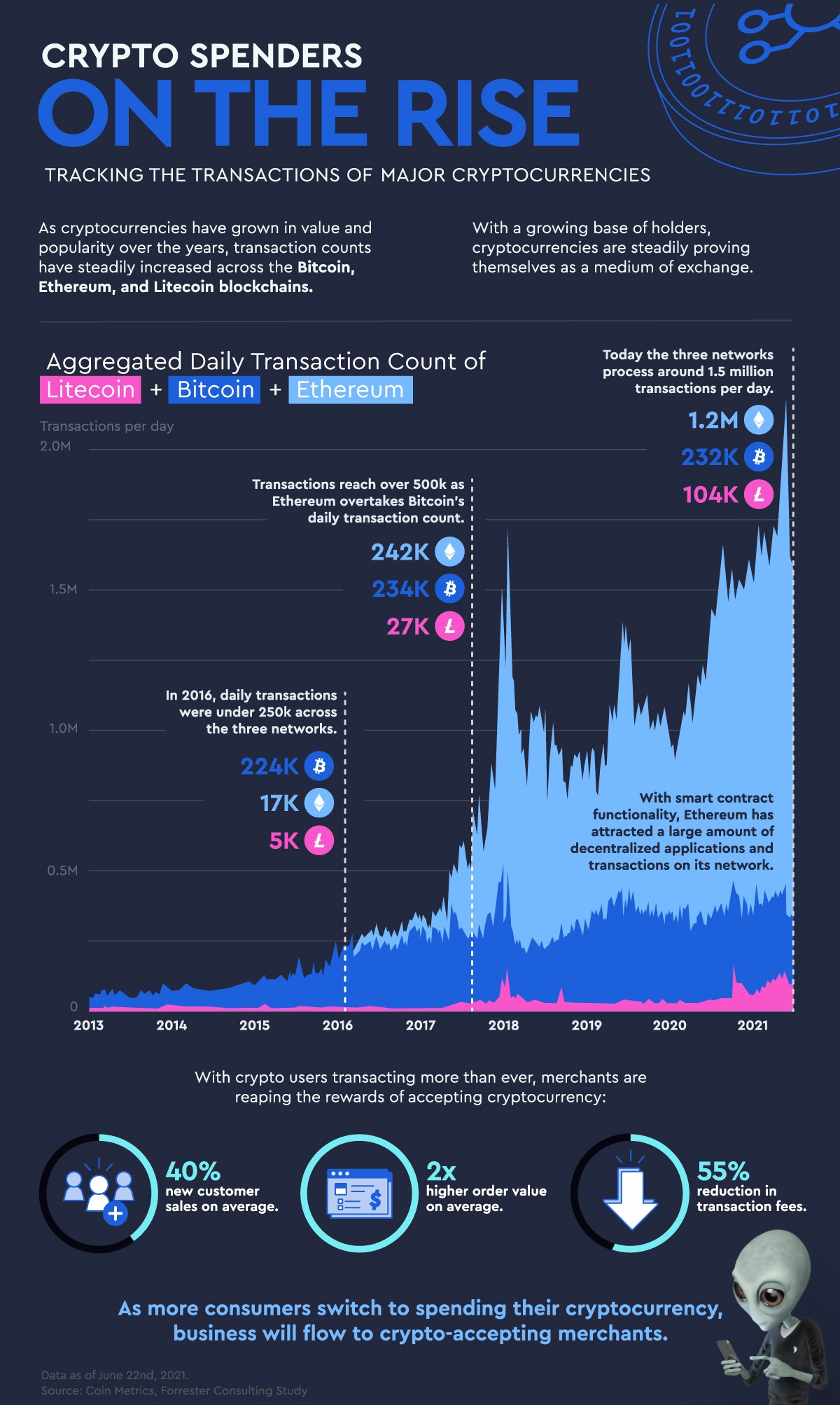
The Mass Adoption of Cryptocurrencies
The rise of cryptocurrencies over the past decade has been nothing short of meteoric. From being a niche interest for tech enthusiasts to becoming a serious contender in the financial world, the trajectory of cryptocurrencies is undeniable. But what are the factors driving this shift towards mass adoption?
The Appeal of Decentralization
Cryptocurrencies, by nature, operate on decentralized platforms. This means they aren’t controlled by any central authority, such as governments or financial institutions.
For users, this means increased autonomy over their money and financial transactions. It also offers protection against potential mismanagement of traditional financial systems and centralized control.
Technological Advancements & Scalability
The early days of cryptocurrency, especially Bitcoin were marred by concerns about scalability and the potential inability to handle a high volume of transactions efficiently.
With advancements like the Lightning Network for Bitcoin and sharding for Ethereum, the capacity to process more transactions quickly has grown, drawing more users to the crypto space.
Inclusion in Mainstream Financial Products
As the legitimacy of cryptocurrencies has grown, they’ve been incorporated into traditional financial products and services.
Cryptocurrency futures, ETFs, and inclusion in portfolio management have brought in institutional investors, adding credibility and driving further adoption.
Increasing Merchant Acceptance
A growing number of merchants and service providers, both online and offline, now accept cryptocurrencies as a form of payment.
This increasing acceptance makes cryptocurrencies more practical for everyday use, gradually transforming them from speculative assets to genuine currencies.
Economic Turmoil and Fiat Currency Concerns
Economic instability in various regions has led people to seek alternative forms of money, with cryptocurrencies being a top choice due to their global nature.
In countries facing hyperinflation or strict monetary controls, cryptocurrencies offer a refuge for wealth preservation and transfer.
Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
The DeFi movement, based primarily on Ethereum’s platform, offers decentralized lending, borrowing, and other financial services without traditional intermediaries.
As more users see the potential of earning interest, borrowing, and more through decentralized platforms, the adoption of related cryptocurrencies has surged.
Growing Awareness and Education
More educational resources are available now than ever before, making it easier for newcomers to understand and engage with cryptocurrencies.
As more people become informed about the benefits and potential of cryptocurrencies, barriers to entry are reduced, leading to wider adoption.
Regulatory Clarity
Though the relationship between cryptocurrencies and regulators has been complex, certain regions have started to provide more explicit regulatory frameworks.
Clearer regulations can reduce the perceived risk associated with investing in or using cryptocurrencies, encouraging more mainstream users and institutions to participate.
Hurdles Cryptocurrencies Still Have to Face
Since their inception, cryptocurrencies have been hailed for their potential to revolutionize the financial landscape. They bring to the table decentralization, enhanced security, and global reach. However, like all innovations, they come with their set of challenges. While some hurdles have been overcome since the early days of Bitcoin, others persist and new ones emerge.
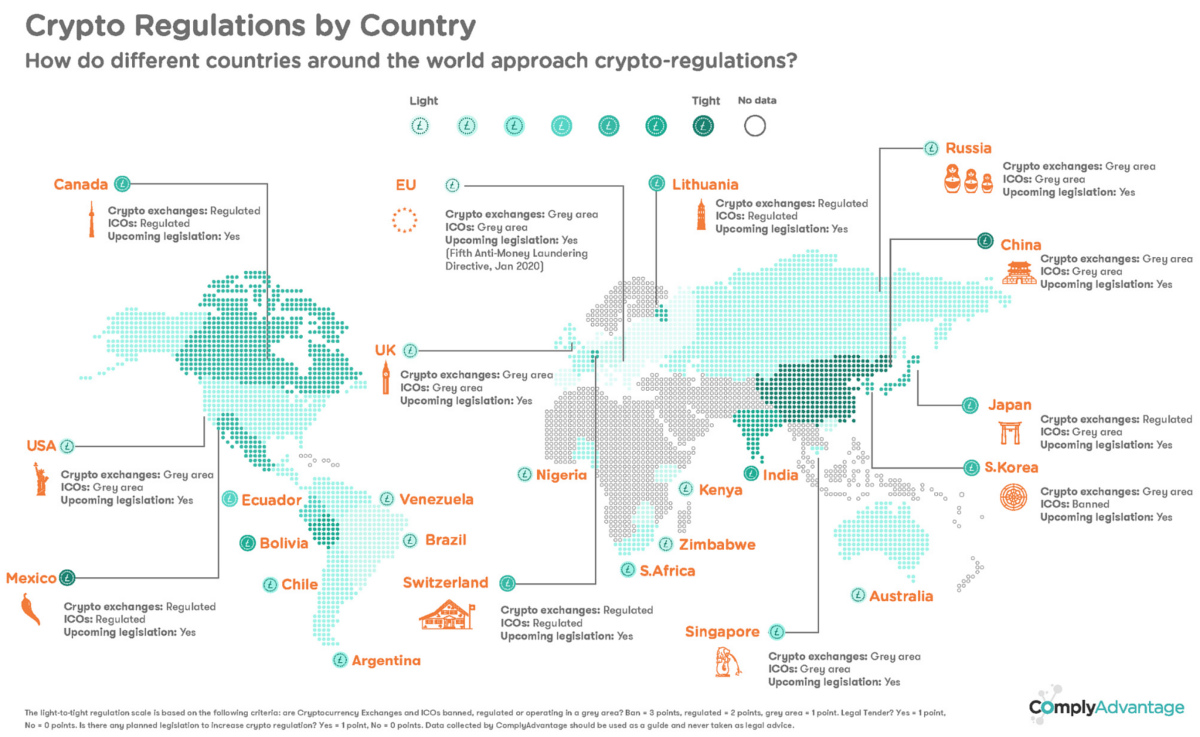
Regulatory Uncertainty
Governments worldwide are grappling with how to classify and regulate cryptocurrencies. Are they assets? Currencies? Securities?
Uncertain regulatory environments can hinder institutional adoption, stifle innovation, and occasionally lead to abrupt market reactions based on regulatory news or rumors.
Scalability Issues
Many popular cryptocurrencies, including Bitcoin and Ethereum, have faced challenges related to scaling their networks to accommodate increasing numbers of transactions.
Congested networks can result in delayed transaction times and higher fees, making them less appealing for everyday use.
Volatility
Cryptocurrencies are known for their price volatility, with values sometimes swinging dramatically in short periods.
This volatility can deter mainstream users and merchants from adopting cryptocurrencies, fearing potential sudden losses.
Security Concerns
While blockchain, the underlying technology of cryptocurrencies, is heralded for its security, the broader ecosystem, including exchanges and wallets, has witnessed significant breaches.
High-profile hacks can erode trust in the ecosystem, making potential users hesitant to invest or transact in cryptocurrencies.
Lack of Awareness and Understanding
Despite growing interest, a significant portion of the global population remains unaware or misinformed about cryptocurrencies.
Misconceptions can lead to skepticism or ill-informed decisions, hampering widespread adoption.
Environmental Concerns
Proof-of-work (PoW) cryptocurrencies, like Bitcoin, require considerable energy for their mining processes, leading to concerns about their carbon footprint.
As global attention shifts towards sustainability, energy-intensive cryptocurrencies may face criticism, leading to a push for more eco-friendly consensus mechanisms.
Integration and Usability
For the non-tech savvy, navigating the world of cryptocurrencies – from setting up wallets to ensuring transaction privacy – can be daunting.
If cryptocurrencies are to become mainstream, they need to be as easy to use as current digital payment methods.
Potential “Better” Alternatives
The rapid evolution of the crypto space means newer cryptocurrencies or technologies could potentially offer superior benefits to existing ones.
This can result in a fragmented market with users spread thin across various platforms, making universal acceptance more challenging.
Competition from Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs)
Several central banks are exploring or piloting their digital currencies.
If CBDCs are successfully launched and adopted, they could pose significant competition to decentralized cryptocurrencies, especially in areas like daily transactions.
Conclusion
While the eventual displacement of fiat currency by cryptocurrencies remains a topic of debate, there is little doubt that the financial systems of the future will be vastly different from what we know today. The inherent weaknesses of fiat systems, combined with the advantages offered by cryptocurrencies, suggest that digital assets will play an increasingly significant role in the global economy. Whether they completely replace traditional money or coexist in a new hybrid system, change is undeniably underway.








